Ignition coils operating principle. Ignition coils - structure and principle of operation of the car ignition module How to connect an individual ignition coil
For a gasoline internal combustion engine, the ignition system is one of the determining ones, although it is difficult to single out any main component in the car. You can’t go without a motor, but it’s also impossible without a wheel.
The ignition coil creates high voltage, without which it is impossible to form a spark and ignite the fuel-air mixture in the cylinders of a gasoline engine.
Briefly about ignition
To understand why there is a reel in a car (this is a popular name), and what part it takes in ensuring movement, you need to at least generally understand the structure of ignition systems.
Be sure to read

About all types of ignition systems
A simplified diagram of how the reel works is shown below. 
The positive terminal of the coil is connected to the positive terminal of the battery, and the other terminal is connected to the voltage distributor. This connection scheme is classic and is widely used on VAZ family cars. To complete the picture, it is necessary to make a number of clarifications:
- The voltage distributor is a kind of dispatcher that supplies voltage to the cylinder in which the compression phase has occurred and the gasoline vapors should ignite.
- The operation of the ignition coil is controlled by a voltage switch; its design can be mechanical or electronic (contactless).
Mechanical devices were used in old cars: the VAZ 2106 and the like, but now they are almost completely replaced by electronic ones.
Reel design and operation
The modern bobbin is a simplified version of the Ruhmkorff induction coil. It was named after the German-born inventor Heinrich Ruhmkorff, who was the first to patent a device in 1851 that converts low-voltage direct voltage into high-alternating voltage.
To understand the principle of operation, you need to know the structure of the ignition coil and the basics of radio electronics. 
This is a traditional, common VAZ ignition coil, used for a long time on many other cars. In fact, this is a pulse high-voltage transformer. On a core designed to enhance the magnetic field, a secondary winding is wound with a thin wire; it can contain up to thirty thousand turns of wire.
On top of the secondary winding is a primary winding made of thicker wire and with fewer turns (100-300).
The windings at one end are connected to each other, the second end of the primary is connected to the battery, the secondary winding with its free end is connected to the voltage distributor. The common point of the coil winding is connected to the voltage switch. This entire structure is covered by a protective housing.
A direct current flows through the “primary” in the initial state. When a spark needs to be formed, the circuit is broken by a switch or distributor. This leads to the formation of high voltage in the secondary winding. Voltage is supplied to the spark plug of the desired cylinder, where a spark is formed, causing combustion of the fuel mixture. High-voltage wires were used to connect the spark plugs to the distributor.
The single terminal design is not the only one possible; there are other options. 
- Double spark. The dual system is used for cylinders that operate in the same phase. Let’s assume that compression occurs in the first cylinder and a spark is needed for ignition, and in the fourth cylinder there is a purge phase and an idle spark is formed there.
- Three-spark. The principle of operation is the same as that of a two-terminal one, only similar ones are used on 6-cylinder engines.
- Individual. Each spark plug is equipped with its own ignition coil. In this case, the windings are swapped - the primary is located under the secondary.

How to check the ignition coil
The main parameter by which the performance of the reel is determined is the resistance of the windings. There are average indicators that indicate its serviceability. Although deviations from the norm are not always an indicator of a malfunction.
Using a multimeter
Using a multimeter, you can check the ignition coil according to 3 parameters:
- primary winding resistance;
- secondary winding resistance;
- presence of a short circuit (insulation breakdown).
Please note that only an individual ignition coil can be checked in this way. Dual ones are designed differently, and you need to know the output circuit of the “primary” and “secondary”.
 We check the primary winding by attaching probes to contacts B and K.
We check the primary winding by attaching probes to contacts B and K.
When measuring the “secondary” we connect one probe to contact B, and the second to the high-voltage terminal.
The insulation is measured through terminal B and the coil body. The device readings should be at least 50 MΩ.
It’s not always common for a car enthusiast to have a multimeter at hand and experience in using it; on a long journey, checking the ignition coil using this method is also not available.
other methods
Another method, especially relevant for old cars, including VAZs, is to check the spark. To do this, the central high-voltage wire is placed at a distance of 5-7 mm from the motor housing. If a blue or bright purple spark flashes when you try to start the car, the reel is working normally. If the color of the spark is lighter, yellow, or absent altogether, this may confirm that it is broken or the wire is faulty.
There is an easy way to test a system with individual coils. If the engine stalls, you just need to disconnect the power to the coils one by one while the engine is running. We disconnected the connector and the operating sound changed (the machine stalled) - the coil is fine. The sound remains the same - the spark does not reach the spark plug in this cylinder.
True, the problem may also be in the spark plug itself, so for the purity of the experiment, you should swap the spark plug from this cylinder with any other.
Connecting the ignition coil
If during dismantling you did not remember and did not mark which wire went to which terminal, the ignition coil connection diagram is as follows. The terminal with the + sign or the letter B (battery) is supplied with power from the battery, and the switch is connected to the letter K. The colors of the wires in cars may vary, so it is easiest to track which goes where.
The correct connection is important, and if the polarity is incorrect, the reel itself, the distributor, or the switch can be damaged.
Conclusion
One of the important components in a car is the bobbin, which creates high voltage to produce a spark. If dips appear in the engine’s operation, it begins to stall and simply run unstably – this could be the cause. Therefore, it is important to know how to check the ignition coil correctly, and if necessary, using the old-fashioned method, in the field.
ZnanieAvto.ru
Ignition coil: device, principle of operation and signs of malfunction
The ignition coil is the second element in the sequence of the car engine ignition system. The operation of the ignition coil is similar to the functions of a transformer and is based on the conversion of low voltage voltage from the vehicle's rechargeable (starter) battery into high voltage voltage generated for the spark plugs, resulting in ignition of the air-fuel mixture.
Ignition coil device
The coil consists of primary and secondary windings, an iron core and an insulated housing. On a core made of thin metal plates, two windings of thick and thin copper wire are wound.

The principle of operation of the ignition coil is similar to that of a transformer. When voltage is applied to the primary winding circuit, a magnetic field is created in the coil. The secondary winding of the ignition coil is self-inducing and generates voltage. The transformed voltage is supplied to the spark plugs through a switchgear, and the high-voltage discharge continues until the energy created by the coil is spent.
Types of coils
Today, there are a sufficient number of types of ignition coils that can be installed both on old domestic cars with carburetor engines and on more modern cars with direct fuel injection.

Housing ignition coils are installed on vehicles with mechanical ignition distribution, where the distributor, rotating, supplies high-voltage voltage to each spark plug in a certain sequence. This method of switching and voltage distribution is not used in the modern automotive industry due to its short service life and low reliability.
A coil with electronic ignition distribution, or a distribution coil, does not require an additional contact cascade breaker for its operation, because with the development of technology in microelectronics, it has become possible to integrate such an ignition breaker into the coil itself. This coil is suitable for cars with mechanical ignition distribution.
A dual-spark ignition coil allows spark plug voltage to be generated simultaneously in two engine cylinders per crankshaft revolution, without the need for coordination between the ignition system and the camshaft. It is advisable to use such coils only in engines with an even number of cylinders, for example, for an engine with four cylinders you will need two coils, with six - three, respectively, with eight - four.
 Double spark ignition coil
Double spark ignition coil The "smart" plug ignition coil is single-spark and is installed directly on each spark plug. The design and functional characteristics of such a coil make it possible to avoid the use of high-voltage wires in the system, but it requires connecting clamps (terminals) designed for high voltage. Due to their compactness, these coils are used in cars with a small amount of free engine compartment space, but compact does not mean ineffective. The plug coil can easily compete with its brothers.
 Plug-in ignition coil device
Plug-in ignition coil device The advantages of the reel are:
- The widest range of ignition timing settings.
- Diagnosis of misfires from the primary and secondary windings.
- Spark extinguishing in the secondary circuit using a high-voltage diode.
Such devices are used for engines with any number of cylinders, but synchronization with the position of the camshaft using an appropriate sensor is strictly required.
Coil malfunctions and their diagnosis
The ignition coil is a fairly reliable element of the system, but it is not immune to all sorts of malfunctions, often associated with non-compliance with operating rules. Let's look at the most common signs of a faulty ignition coil:
- Unstable engine speed at idle.
- Engine stalls when the throttle valve is opened sharply.
- The "Check" light came on.
- No spark.
First of all, if a breakdown occurs in the ignition system, you should visually inspect the coil and look for cracks, charring, and also check its temperature and humidity. If the ignition coil heats up, this may indicate that an interturn short circuit has occurred and the device must be replaced. High humidity in the area where the ignition coil is located can also affect engine performance. If the coil is dry, without cracks, soot and not hot, but there is still a malfunction in the system, it is necessary to diagnose it.
If the car does not start, that is, the starter cranks, but the engine does not pick up the ignition, this may mean that there is no spark from the ignition coil.
- How to check the ignition coil for functionality for a contactless ignition distribution system? It is necessary to disconnect the high-voltage wire located in the center of the ignition distributor and position this wire at a distance of approximately 5 millimeters from the metal body of the engine. Then we turn the engine crankshaft with the starter and observe the presence of a spark in the gap between the contact part of the high-voltage wire, which was disconnected from the distributor, and the engine housing (ground).
- In a contact ignition system, cranking of the crankshaft by the starter is excluded from this procedure, namely: remove the ignition distributor cap and set the voltage breaker contacts to the closed state. Then we turn on the ignition with the breaker lever, open and close the contacts. The presence of a spark in the gap between the wire and ground tells us that the ignition coil is working properly.

If the ignition coil diagnostics reveal a lack of spark, then you need to check the resistance of the ignition coil. To do this, you will need a regular multimeter or ohmmeter and a technical passport for the coil, where you can see its parameters, including the resistance of the windings. Before checking the ignition coil, disconnect all the wires and measure the resistance of both windings one by one, while the resistance of the primary winding should be less than that of the secondary. If during the measurements it turned out that the resistance of both windings corresponds to the factory parameters, and when checking “for a spark” there was no spark, then we can conclude that an insulation breakdown between the turns and the housing has occurred.

Replacing the ignition coil
If the coil malfunctions and cannot be restored, it must be replaced. You can buy exactly the same original one, or you can choose a similar one, but their characteristics should not differ by more than 20-30 percent, and also have the same fastening and design. For example, for domestic cars VAZ-2108 - 2109 with electronic coils 27.3705 from a domestic manufacturer, coils 0.221.122.022 from Bosch, which are not much different in parameters, are suitable. In this case, the spread of parameters will be from 10 to 15%.
To summarize, it can be noted that when writing the article, real information was used about the problems that each driver faced. All coils are practically the same from each other in terms of their operating principle, but not all of them are interchangeable, for example, coils with mechanical ignition distribution cannot work with contactless distribution and vice versa.
SwapMotor.ru
Operating principle and design of the ignition coil
Welcome, friends, to the DIY car repair website. The ignition coil (module) is one of the key components of the car, ensuring timely ignition of the air-fuel mixture and normal engine operation.

Ignition coil device
The purpose of the ignition coil is to increase the vehicle's standard voltage (12 volts) to a higher potential, which ensures that a powerful spark appears between the spark plug electrodes. The result is ignition of the working mixture, movement of the pistons, rotation of the crankshaft and movement of the machine.
Design features and types of ignition coil
The design of the ignition coil is extremely simple. The basis of the unit is a conventional two-winding transformer. Between the “primary” and “secondary” there is a steel core. The entire structure is protected by an insulated casing.
Each winding has its own characteristics:
For the “primary”, a thick wire made of high-quality copper is used. The number of revolutions is 100-150. Input voltage - 12 Volts;
- the “secondary” is wound on top of the primary winding. It contains from 15 to 30 thousand revolutions. The material used (as in the first case) is copper wire, but with a different cross-section.
The system described above is typical for different types of coils - individual and dual type. The operating voltage on the secondary side of the device is 35 thousand volts.
The role of the insulating composition is performed by transformer oil, which is located inside the product. In addition to insulating, oil performs another function - it protects the device from overheating.
Types of coils can be:
1. General. Such devices are used in cars where there is or is no distributor. The design of this product is described in the section above. In particular, the device consists of two windings, a steel core and an outer casing. The generated impulse is sent to the electrodes of the spark plugs.
2. Individual. The devices are used in cars with electronic ignition. The peculiarity is the presence of a “primary” inside a “secondary”. An individual device is installed directly on each spark plug.
3. Double. They are used in cars with electronic ignition. A special feature of this device is the presence of double wires, which guarantee the supply of a spark to two combustion chambers at once. In this case, there will be only one chamber in the compression stroke, and for the second, ignition is idle.
How does an ignition coil work?
Knowing the structure of the unit, it is much easier to understand the principle of operation of the ignition coil. The potential from the battery (12 Volts) is supplied to the “primary”. After this, a magnetic field is created in the transformer.
The periodically supplied voltage is interrupted by a breaker, which leads to a reduction in magnetic fluxes and the formation of an EMF in the windings.
Now let’s remember the physics course, where the law of EMI (electromagnetic induction) is well explained. It says that the size of the EMF directly depends on the number of turns in the circuit. Consequently, a higher voltage is formed in the “secondary”.
The resulting potential is transferred directly to the electrodes of the spark plugs, which contributes to the appearance of a spark and ignition of the prepared combustible mixture.
In older VAZ cars, the voltage from the unit was distributed to all spark plugs using a distributor. The downside of the device is insufficient reliability, so modern devices are combined into a common system and distributed to each candle separately.
Basic failures and methods for diagnosing the coil
During operation, the following malfunctions of the ignition coil are possible:
- Engine malfunctions;
- instability of idle speed;
- difficulties in adjusting idle speed;
- problems with starting the engine or inability to start the engine (this is especially true in cold weather);
- lack of spark in one or more spark plugs;
- twitching when starting to move and during the trip.
If you suspect a malfunction, it is important to know how to check the ignition coil. Proceed according to the following algorithm (using the example of VAZ-2108-2109):
1. Prepare the tools you will need to complete the work. Here you need a tester (you can use a regular multimeter, which has an ohmmeter mode), as well as an “eight” key (it can be open-end or ring-type).
2. Carry out preparatory work. In particular, check the unit without removing it from the vehicle. To do this, remove the “minus” from the power source, remove the wire coming from the module, disconnect the wires that are connected to the coil terminals.
To unscrew the screws, use an "eight" wrench. At the same time, remember the position of the wires so that when returning them to their place you will not make a mistake.
The verification itself is carried out in several stages:
1. Diagnostics of the serviceability of the primary winding. Connect one multimeter probe to output “B”, and the second to output “K” (this is the beginning and end of the primary winding). Set the switch to resistance measurement mode (it should be at 0.4-0.5 Ohm).
2. Diagnostics of the serviceability of the turns of the secondary winding. To check this part of the coil, connect the multimeter probe to output “B”, and the second one to the terminal of the wire itself. Measurements should show a resistance of 4.5-5.5 kOhm.
3. Diagnostics of the integrity of the insulating coating. Connect one of the tester probes to output “B” of the device, and touch the outer part with the other. In this case, the resistance should be about 50 mOhm or more. If at least one of the 3 checks has failed, then the coil needs to be changed.
When operating the ignition coil, you need to consider several useful tips; perhaps someday they will come in handy.
Do not leave the ignition on for a long time (provided that the engine is not running). Such an oversight leads to a decrease in the life of the coil and its rapid breakdown.
Clean and diagnose the condition of the product. Check the quality of fixation of the conductors. Pay special attention to wires carrying high voltage. In addition, make sure that there is no moisture entering the casing or the inside of the device.
Do not throw wires away from the device while the ignition is active. If this must be done, use special gloves.
As can be seen from the article, the design and operation of the ignition coil, as well as its maintenance, should not cause problems even for a novice car enthusiast. The main thing is to be attentive to your car, pay attention to the malfunctions described above and promptly check the ignition coil for defects.
If any breakdowns are detected, try not to delay replacing the unit. Otherwise, troubles with starting the engine may occur on the road.
RemontAvtoVaz.ru
Ignition coil design and operating principle
Hello again, friends! Continuing the topic of such a complex car system as electronic ignition, I propose to disassemble its integral and, without a doubt, main element called the ignition coil! After all, it is precisely this that guarantees the appearance of the required voltage on the electrodes of the spark plug, which ensures the ignition of the combustible mixture and, accordingly, the movement of the vehicle itself. In other words, the mechanism increases the standard 12 volts a huge number of times, up to 35 thousand volts. Due to what and exactly how this happens I will try to explain to you today.
Design features

So what is an ignition coil? By and large, this is an ordinary car transformer with a simple structure! Its device consists of a two-layer insulated winding and a steel core. The first such layer is designed for low-voltage pulses (6-12 V), it is made of copper wire of larger diameter with a number of turns from 100 to 150.
The second layer is already created from small-section wires and is located under the primary winding, contacting one end with its negative terminal. Due to the huge number of turns (up to 30 thousand) and the position of the copper wire, a high pulse voltage is generated. Current is supplied from the positive end of the secondary winding through the center terminal of the coil. In turn, the metal core is placed exactly in the middle of the ignition coil, significantly increasing the magnetic field of the windings.
All the elements described above are sealed in a special housing, which every car enthusiast can see under the hood of his car, whether it’s on the injector or the carburetor. Insulation plays a special role in such a structure, and in electrical engineering in general. It is provided by a special housing cover, on which, by the way, there are terminals for the primary and secondary windings (more details in the diagram), as well as transformer oil. The liquid also performs another important function - cooling.
What types of ignition coils are there?
At the moment, friends, your humble servant has counted as many as three types of ignition coils. They all play the same role, but despite this, they have a different design, and sometimes even a different principle of operation. Now, I suggest you spend enough time on each of them!
General type – classic

A general type ignition coil works in tandem with a special distributor (distributor), which conducts the impulse to the desired cylinder. It is used on cars with any ignition system. The entire process of creating a spark looks like this:
- The voltage from the battery supplied to the device follows the turns of the first layer of wire.
- Thus, a magnetic field is created, due to which a high voltage pulse is generated on the secondary winding.
Note: to calculate the output voltage, the number of turns of the second layer of wire should be multiplied by the field induction of the primary winding. This means that the more turns on the secondary winding, the correspondingly higher the output current.
- The iron core, simply by being in the housing, increases the magnetic field, and with it the voltage.
- Transformer oil helps reduce the temperature from possible current heating.
Due to the fact that the cover of such an ignition coil is hermetically sealed to the body, the device is practically not subject to repair. To be sure that it is faulty, you need to measure the resistance of its turns. Each coil has its own indicator and you need to know it; possible deviations during measurement will mean failure of the unit.
Double or dual coil

The operation of this type of ignition coil does not require a distributor in the system and can be connected to the spark plugs in two ways:
- The pulses are supplied through several high voltage wires.
- Using one high voltage wire and ferrule.
Despite the fact that the body differs significantly from the general type of coils, the internal structure is almost identical to them. The only difference is a pair of pins for sending pulses. Yes, you heard right, there are two outputs and, accordingly, the spark goes to two spark plugs at once. You know that the simultaneous end of the compression stroke in two cylinders at once is unrealistic? If not, now you know for sure.
So, at the moment of spark ignition, the end of the stroke will be in only one cylinder, where the air-fuel mixture will be successfully ignited. In the second, the spark will be absolutely stupid, in other words, idle. However, after some time everything will change exactly the opposite.
You probably noticed that we were talking about only two cylinders, but how does a twin coil cope with 4? No way, such units are used mainly in motorcycles with electronic ignition, but for a car there is a four-terminal coil or, in simple terms, an ignition module. We discussed it in the last article, remember?
Custom ignition coil

This type of ignition coil has this name for a reason. Each glow plug of the power unit receives its own, individual ignition coil, hence the name. Everything looks quite simple; the device is installed directly on the candle itself. Thus, there is no need to use armored wires in the chain, but even though the device has a completely different body, the principle of its operation remains the same. Each individual coil differs in the design of its core, hence its two types:
How does this mechanism work in general? The essence is basically the same, but in order to recreate what turns out to be an already outdated Soviet coil in more compact dimensions and at the same time make it an order of magnitude more efficient, I had to change something.
- There are now two cores, the inner one remains in the middle, and the outer one is carried out beyond the winding.
- The winding is carried out, as before, in two layers, but the only difference is that the secondary is located on top of the primary.
- Diode - attached to the secondary winding and protects both layers from high loads.
In conclusion
Well, what can I say, friends, this type of ignition coil is definitely lighter than its predecessor, both literally and figuratively! It is compact, requires less energy and is more reliable. In my opinion, the leader in this race is obvious.
I repeat: almost all ignition elements are difficult to repair, and the ignition coil is no exception. Replacement, in most cases, is just a replacement.
We disassembled the ignition coil itself inside and out. Structure, principle of operation, varieties - we talked about everything, it seemed. But for some reason I want to talk about it and talk about it! Therefore, in a future article, I will tell you how to identify a failed unit, how to do everything carefully and correctly! Signs of a faulty ignition coil, its own diagnostics and much more in the next publication! On this I put a bold ellipsis and look forward to new meetings on the pages of our blog! See you later…
Best regards, Maxim Markov!
carsmotion.ru
Ignition coil in car systems

The ignition coil (let's call it the ignition coil for short) is one of the most important components of any ignition system, the main task of which is to convert low voltage currents into high voltage currents to produce a high voltage pulse at the spark plug.
Sometimes, both in everyday life and in specialized literature, another name for the coil is found - “reel”.

Essentially, the ignition coil is a transformer that has a high transformation ratio. The higher the voltage in the secondary winding, the higher the value of this coefficient. However, an increase in the coefficient usually entails an increase in the dimensions of the device, which limits this process, since there is not so much space in the engine compartment of a modern car. The reel must also have the ability to quickly charge after delivering a high-voltage pulse to the spark plug, especially at increased vehicle engine speeds.
Design and principle of operation of the ignition coil
 In fact, the design of ignition coils (IC) has not changed since the very moment the first car appeared. As mentioned above, the ignition bobbin is a transformer (a simplified Ruhmkorff coil) consisting of two windings, usually made of a copper alloy. The primary winding is made of thicker wire and has about 100-150 turns, and the secondary winding consists of thin wire and has up to 30,000 turns. Since the primary winding generates more heat than the secondary, it is located closer to the transformer core.
In fact, the design of ignition coils (IC) has not changed since the very moment the first car appeared. As mentioned above, the ignition bobbin is a transformer (a simplified Ruhmkorff coil) consisting of two windings, usually made of a copper alloy. The primary winding is made of thicker wire and has about 100-150 turns, and the secondary winding consists of thin wire and has up to 30,000 turns. Since the primary winding generates more heat than the secondary, it is located closer to the transformer core.
 Nowadays, bobbins are often supplemented with additional resistance in order to increase the voltage in the secondary winding while maintaining a relatively small size of the device.
Nowadays, bobbins are often supplemented with additional resistance in order to increase the voltage in the secondary winding while maintaining a relatively small size of the device.
The bobbins can have either bitumen or oil insulation, the latter allowing the production of ignition coils of various configurations. Various synthetic materials, which are widely used today in the manufacture of this element of the ignition system, provide good adhesion between all parts of the coil. Previously, an open magnetic circuit was used in the design of ignition coils, but nowadays its closed version is also used.
The operating principle of this device is quite simple. A low voltage direct current flows in the primary winding of the transformer (12V, and on older cars and motorcycles - 6V), and at the moment when a spark is needed at the spark plug, the contacts of the primary circuit open.
Depending on the type of ignition system, contact interruption occurs using a mechanical device or using transistor or thyristor switches (electronically). According to the law of electromagnetic induction, current pulses with a high output voltage are created in the secondary winding, which can be calculated by the formula: voltage value = number of turns * induction per turn.
Connecting the ignition coil - what is important to pay attention to

Replacing a faulty ignition coil on your own, in principle, is not so difficult, especially if you follow a number of recommendations. The first of them is that, as with any other interventions in the operation of electrical devices and systems of the car, it is necessary to turn off the power to the on-board network. To do this, simply remove the terminal marked “-” from the car battery.
If you are not completely sure that the reel is connected correctly, then it is better to find a diagram for a specific car brand on the Internet, fortunately this is not difficult to do nowadays, or contact a specialist, since an incorrectly connected device may itself fail, and cause damage to other ignition components.
The second, but no less important recommendation is that before disconnecting the old ignition coil, you should remember, or better yet, sketch where and how the high-voltage wires are connected, especially when replacing an ignition module that has several coils and many wires. When connecting the reel or ignition module, all fasteners and contacts should be tightly tightened, since gaps in them will lead to significant current leaks.
Diagnostics and possible short circuit faults
Despite the fact that modern ignition coils are quite reliable devices, sometimes they still fail. Moreover, very often the causes of failure are incorrect operation or incorrect actions when searching for faults in the operation of the entire ignition system.
So, for example, checking the spark on the spark plugs with the main high-voltage wire that goes from the coil to the breaker disconnected can lead to the combustion of not only the coil itself, but also damage to other expensive components, especially if we are talking about the electronic ignition system. Using poor quality or faulty spark plugs can also cause the ignition coil to break. This happens due to back gases that corrode the silicone (or rubber) tip of the reel/ignition module.
 You can check everything with the following device, which is shown in this photo.
You can check everything with the following device, which is shown in this photo.
The most common sign of a coil malfunction is its high temperature, even when the engine is turned off.
The reason for this may be a rather long active position of the key in the ignition switch, leading to an increased load on the coil. This, in turn, causes overheating of the bobbin windings, which, if repeated frequently, can cause them to dry out and crumble. Overheating can also occur due to wear on the silicone tips, causing current leakage.
Separately, it is worth noting that although driving with a faulty ignition coil or coils is sometimes possible, this can lead to not very good consequences. For example, the catalytic converter in the exhaust system may melt, and fuel consumption may increase by up to 25% due to a drop in efficiency and a decrease in engine power.
There is no spark from the ignition coil - what to do?
One of the most unpleasant moments for any motorist is the lack of spark on the ignition coil. However, the reason for this does not always lie in the bobbin itself. Before checking the coil, it is necessary to conduct a visual inspection of the engine compartment, paying special attention to the condition of the high-voltage wires, the ignition control unit (in an electronic system) and the distributor (in contact and non-contact systems). If there are traces of contamination (stains from machine oil, sand or water stains), they must be carefully removed with a clean, dry cloth. After this, you need to inspect and check all contacts and wiring insulation; if damaged areas are found, replace parts and components with new ones.
 If, after the above steps, a spark still does not appear on the coil, then you need to make sure that the spark plugs, the computer and the breaker-distributor are working properly. It is better to start checking with the spark plugs. Having removed the spark plug wire from each of them in turn, you should bring it at a distance of 5-8 mm to any unpainted metal part of the body and turn on the ignition. When the starter rotates, a spark should appear, and its glow should be a pale bluish hue. If the spark is bright red, orange, white, or completely absent, then the issue is indeed a faulty ignition coil.
If, after the above steps, a spark still does not appear on the coil, then you need to make sure that the spark plugs, the computer and the breaker-distributor are working properly. It is better to start checking with the spark plugs. Having removed the spark plug wire from each of them in turn, you should bring it at a distance of 5-8 mm to any unpainted metal part of the body and turn on the ignition. When the starter rotates, a spark should appear, and its glow should be a pale bluish hue. If the spark is bright red, orange, white, or completely absent, then the issue is indeed a faulty ignition coil.
If there is a normal spark on the spark plugs, you should proceed to checking the distributor, first inspecting its cover, which should be without any mechanical damage. If it is heavily soiled, it should be cleaned with a clean cloth soaked in gasoline. The central carbon contact of the distributor should not “freeze”; this can be checked by simply moving it with your finger.
Among distributor malfunctions, there are often problems with the rotor, whose insulation may be damaged. To check its condition, you need to disconnect the central high-voltage wire from the rotor and manually open and close the breaker contacts. If the rotor is working properly, there will be no sparks in the gaps.
How to check the ignition coil?
As for checking ignition modules that have several coils, this is somewhat more complicated than assessing the condition of just one coil.
The simplest method is to disconnect the connectors from each coil one by one while the engine is running. When you disconnect the wire from a working coil, you will hear dips in the operation of the motor (“triples”), but disconnecting the faulty coil will not have any effect. It is this coil that should be replaced. Spark plugs can also help find a faulty coil. As a rule, the spark plug electrodes on a defective reel have black carbon deposits. Many modern cars have a self-diagnosis system, and a malfunction in one or another ignition coil will be displayed on the instrument panel in the form of a special code, the meaning of which can be determined by the service book.
To make sure that the coil is broken, you can remove it from the car and measure the resistance of the primary and secondary windings. However, it is better to carry out these actions on most modern car models in a specialized car service, since ineptly disconnecting the coil or ignition module can lead to failure of the ECU.
 On cars with one ignition coil, the check will take a little less time, especially since on ignition systems without electronic control units, this part can be removed independently without fear of damaging anything. After removing the coil, the first step is a visual inspection. The surface of the housing should not be covered with a thick layer of dirt and soot, or have any mechanical damage. Dirt, oddly enough, is one of the main causes of current leaks. Next, you should check the coil for internal breaks in the windings, for which you will need to ring it using a special device - an ohmmeter. This operation must begin with the primary winding, the resistance of which, if working properly, should be much less than the secondary.
On cars with one ignition coil, the check will take a little less time, especially since on ignition systems without electronic control units, this part can be removed independently without fear of damaging anything. After removing the coil, the first step is a visual inspection. The surface of the housing should not be covered with a thick layer of dirt and soot, or have any mechanical damage. Dirt, oddly enough, is one of the main causes of current leaks. Next, you should check the coil for internal breaks in the windings, for which you will need to ring it using a special device - an ohmmeter. This operation must begin with the primary winding, the resistance of which, if working properly, should be much less than the secondary.
If the above steps did not help identify the malfunction, then in this case there is one more method. You will need to connect the primary winding of the coil to a DC source (battery) and connect in parallel a capacitor having exactly the same capacitance as that installed in the ignition system. Connect a spark plug to the secondary winding and turn on the power source several times. The appearance of a characteristic crackling sound will indicate the presence of breakdowns in the winding of the device.
Repair and replacement - prices in Russia and CIS countries
 The average cost of repairs and replacement of ignition coils/modules in auto repair shops in Russia and the CIS countries in terms of Russian currency:
The average cost of repairs and replacement of ignition coils/modules in auto repair shops in Russia and the CIS countries in terms of Russian currency:
- replacing the silicone coil tip – from 100 rubles;
- replacement of the ignition coil – from 200 rubles;
- replacement of the ignition module – from 250 rubles;
- diagnostics of the ignition coil/module operation – from 200 rubles
Prices do not include the cost of replacement components.
What are the best ignition coils?
 Nowadays, when the economy in the post-Soviet space is an open system, you can find quite a lot of analogues of any type of product. Without exaggeration, the same can be said about ignition coils.
Nowadays, when the economy in the post-Soviet space is an open system, you can find quite a lot of analogues of any type of product. Without exaggeration, the same can be said about ignition coils.
In addition to original bobbins for a particular car model, the automobile spare parts market also offers universal analogues from various manufacturers, including Chinese and Russian factories.
There is no clear answer to the question of which ignition coils are the best, since certain models have both a number of advantages and some disadvantages. So, for example, one coil will serve for a long time and properly, but its cost will also be high, while the other will be somewhat cheaper, but will last a shorter period.
However, in our age, when cars change quite often, installing “eternal” parts is also not always advisable.

- ATS 04473 high-voltage reel LADA Priora 1.6i/Kalina – from 700 rubles;
- BOSCH 0221504473 ignition coil LADA Samara/110-12/Priora/Kalina – from 1,400 rubles;
- BOSCH 0221504473 ignition coil separately for spark plug VAZ 2112 1.6L – from 1,750 rubles;
- HUCO 133826 ignition coil LADA Priora/Kalina – from 1,350 rubles;
- BOSCH 0221503485 ignition coil FORD Fiesta/Fusion/Focus II – from 1,580 rubles;
- HUCO 138809 ignition coil FORD Mondeo III – from 1,700 rubles;
- CONCORD CI-8048 ignition coil FORD Fiesta/Fusion/Mondeo II,III/Focus II – from 2,250 rubles;
- CHAMPION BAE409A/245 ignition coil RENAULT Megan II, NISSAN Almera Classic – from 3,000 rubles;
- SWAG 60 92 1524 ignition coil for RENAULT 1.4 - from 4,500 rubles;
- BOSCH 0986221001 ignition coil for RENAULT 1.6 - from 3,500 rubles;
- BOSCH F 000 ZS0 221 ignition coil for RENAULT 1.4 – from 2,500 rubles;
- ASAM 30179 ignition coil RENAULT Logan/Clio/Megane 8V/Kangoo – from 1,800 rubles;
- HUCO 133846 ignition coil TOYOTA Avensis/Corolla – from 2,000 rubles;
- BOSCH 221504020 ignition coil TOYOTA Aygo/Rav 4/ Corolla/ Yaris – from 2,500 rubles;
- BREMI 20166 ignition coil CHEVROLET Aveo, DAEWOO Matiz – from 1,500 rubles;
- AMD AMDEL414 ignition coil CHEVROLET Captiva/Aveo 1.4/ Lacetti 1.8 and 2.0/ Lanos/ Evanda – from 1,400 rubles.
The ignition coil or popularly “bobbin” is a component of the ignition design. It converts the low frequency voltage coming from the battery or car generator into a high one. The primary role of the ignition coil is to generate an electrical pulse on the spark plug.
Structure
The ignition coil is essentially an automobile transformer. The ignition coil device is enclosed in a two-layer winding of cables with insulation of each layer. The first layer of the winding has a relatively small number of turns (from 100 to 150) of a thick copper cable, designed for pulses with low voltage (in relatively new machines - 12 volts, and in old ones - 6). The second layer of the ignition coil winding is located under the initial winding, which is created from small-section wires with a large number of turns - from 15 to 30 thousand, due to which the highest pulse voltage with a high coefficient occurs.
An iron core is placed in the center of the ignition coil, which increases the magnetic field of the windings. The entire structure is enclosed in a frame with a special lid that provides insulation. The insides of the mechanism are filled with transformer oil to prevent current heating.
On older vehicles, the coils were made with a non-closing magnetic cable, while modern cars are made with a short-circuiting one.
Operation
The principle of operation of the ignition coil is to transmit the required current pulse to the distributor (distributor) through a high-voltage cable, from which the voltage is uniformly directed through the same high-voltage wires to a separate one. Next, a spark is formed at the electrodes, igniting the fuel.
Scheme of operation of a 2-spark device
A constant voltage pulse passes through the first layer of the winding. At the moment when the piston reaches the top dead mark, the breaker contacts on the first winding open and voltage is supplied to the second winding. Subsequently, the impulse is transmitted through the central terminal to the distributor, and then to the spark plugs.
Today, remote ignition coils for a separate spark plug (as many cylinders, as many transformers) are actively used.
Customized coil type
An individual ignition coil has found its application in the direct ignition electrical circuit. Similar to a conventional car transformer, it includes a first and second layer of winding. However, there is one main difference - the first layer of the winding is now placed in place of the second, and the second in place of the first (and not vice versa, as in the standard scheme). In the center of the primary winding there is an inner core, and the outer one, respectively, on the surface of the secondary.
This design may have electrical igniter elements. The current from the second winding is directly transmitted to the spark plug through a tip consisting of a high current rod, a spring and insulating material. Rapid voltage cutoff in the second winding is performed by a high current pulse diode.
Additional resistor
Often, in parallel with the operation of the first winding, an additional resistance is started, which is considered an additional resistor.
At reduced speeds of the power unit, the contacts of the breaker are closed for a long time, so an excessive amount of current flows through the winding, heating the transformer. On the steel coil of the resistor, during the heating process the temperature indicator of the electrical resistance rapidly increases. As excess current passes through the coil, the resistance of the resistor coil becomes correspondingly stronger and the voltage is automatically adjusted.
At increased speeds, the contacts are almost always open, there is no excess current, the resistor heats up slightly, and therefore the additional resistance decreases.

At the moment the engine starts, additional resistance is connected to a section of the electromagnetic circuit by the contacts of the starter relay, thus increasing the spark energy.
In some, especially Soviet, cars, in order to start the engine with a discharged battery, it is necessary to forcibly bypass (or, simply put, short-circuit) the resistor with a current-carrying wire.
Malfunctions
The ignition coil is a part with a long service life. Despite this, there is still a possibility of loss of conductive characteristics and failure of this device.
- The more time a transformer is used, the higher the risk of a short circuit in it and, as a result, overheating of the entire part.
- Prolonged operation at temperatures above 150 leads to a non-repairable condition of the ignition coil.
- If the battery does not provide the required power, this also causes the transformer to malfunction. Since for full operation it requires electricity (the minimum coefficient of the required voltage must be at least 11.5 V).
- A damaged wire can also cause problems with the ignition coil.
- Often the mechanism does not generate voltage due to a defect in the insulation. This problem can occur if motor oil or water gets into the transformer through worn seals, causing resistance to increase and the balance between voltage and resistance to be lost.
- The individual device type is sensitive to excessive vibration from the cylinder head. As a result, the coil quickly becomes unusable.

In some cases, the ignition coil can be repaired. But at home it is quite difficult to assess the degree of damage and the percentage of probability of returning its performance characteristics. Therefore, it is recommended not to save money and replace the old device with a new one.
Before installing a new part, it is important to check all contacts and, especially, the high-voltage wire; Make sure there is no rust, corrosion or other damage at the installation site of the vehicle transformer.
Conclusion
Having learned the structure of this part, we can conclude that it has very reliable properties due to its design. The service life of the coils often reaches two hundred thousand kilometers, which is an impressive result.
You don’t need to have any special automotive education to understand that every element included in the structure of the most common means of transportation - a car - even the smallest one, is very important, and in its absence, things can lead to disaster. The ignition system, and especially its true heart - the coil, does not fall into the category of exceptions. Therefore, it is so important to have an understanding of the design of the ignition coil and its operating principle. This will be discussed further.
The ignition coil (otherwise it can also be called a module) is one of the elements of the automobile ignition system, designed to convert low-voltage voltage from the on-board network into a high-voltage impulse. After this, the resulting high voltage causes a spark to form between the electrodes belonging to the spark plug and ignite the fuel-air system.
In general, this mechanism is a transformer that has two windings and can be used in all systems: electronic, contactless and contact. But depending on the type of coil, its structure is characterized by certain transformations. Let's look at these types and their structure.
- Many electronic ignition system designs may use a dual coil. Another name for it is two-terminal. This type has two high-voltage terminals, which cause two cylinders to simultaneously spark. Moreover, one of the cylinders is located at the end of the compression stroke, and in the other the spark occurs idle.
This type may have more than one type of connection to the spark plugs. Thus, this can happen using drives characterized by high voltage levels. And another method is explained this way: when one candle is directly connected through the tip, and the other is connected using the previously mentioned high-voltage wire.
Remarkably, a pair of dual coils can form a unique single mechanism. At the same time, it will have a new name - four-pin, which is hardly worth explaining. 
- An electronic direct-type ignition system is quite satisfied with an individual coil. Installation of this type is carried out in conjunction with the ignition, whose operation is exclusively electronic control, and the obligatory condition is the absence of any mechanical parts. Ignition in such a coil is carried out using a discharge coming from a capacitor, which is why this system is called direct. The basic functional part of an individual coil consists of turns made of copper wires in order to receive the primary voltage and convert the secondary circuit. It follows from this that a mechanism of this type includes two windings - primary and secondary, with the first located inside the second. The design of the primary winding is characterized by the presence of an internal core, and around the secondary there is an external core.
A custom coil type can house igniter components such as electronic ones. When high voltage is generated in the secondary winding, it is directly applied to the spark plug (this is done using a tip consisting of a high voltage rod, an insulating sheath and a spring). And in order for the high-voltage current in the secondary winding to be cut off as quickly as possible, a diode is installed there, which is also characterized by a high voltage level.
- All three previously named ignition systems can use a common coil. In this case, a mandatory condition for an electronic type system is the presence of a distributor unit.
Like the previously described individual type, this one combines the primary and secondary windings. 
The first consists of no less than one hundred turns of thick copper wire, which was insulated in order to be able to prevent sudden surges in voltage along with a short circuit. Also, the primary winding has two low-voltage characteristics terminals, which are located on the coil cover.
As for the secondary winding, it contains a much larger number of turns (the limit is indicated by the number 30,000), also of copper, but thinner wire. It is noteworthy that in general the secondary winding is located inside the primary winding, in contrast to the individual winding.
The main characteristic of all analyzed types is the resistance of the windings, which varies depending on the model of the mechanism. If the value deviates from the optimal value, this indicates a malfunction of the coil. 
It should also be mentioned that the windings, in order to be able to increase the strength of the magnetic field, are placed around a core made of iron. And all together this forms a structure that is placed in a housing with an insulating lid. In this case, the coil must be filled with transformer oil - this should prevent current heating.
How does it work
The principle of operation of the ignition coil is based on the basic physical laws that were taught in school. It can be characterized as follows: a low-voltage type voltage is sent to the primary winding. All this creates a magnetic field. Sometimes this voltage can be cut off by a breaker, which causes a sharp reduction in the magnetic field along with the formation of an electromotive force in the turns of the coil. 
If you believe the physical law regarding electromagnetic induction, then the magnitude of the electromotive force that arises in this way is proportional to the number of turns in the circuit winding. This can explain the fact that a high voltage pulse is formed in the secondary coil, because there are a large number of turns there. This impulse is sent to the spark plug. Moreover, this process is not typical for the individual type, since this type is installed directly on the candle.
It is thanks to this impulse, transmitted by a coil, that a spark occurs between the electrodes of the spark plug, which causes the fuel-air mixture to ignite. And at the moment when the occurrence of this spark is simply necessary, the contacts in the distributor-breaker open. At the same moment, the primary winding circuit breaks. A high-voltage current appears at the central contact of the coil, after which it is sent again - to the contact opposite which the slider electrode is located at that particular moment. After all this, the circuit is closed, and the impulse passes to the spark plug belonging to one of the cylinders. 
A small recommendation: the coil does not particularly welcome long-term loads, so it is better to turn on the ignition for a long time when the engine does not start. This is a proven fact, the implementation of which will help to maximize the duration of the described mechanism.
Outdated car models had such coils, the voltage from which was supplied to all spark plugs at once using an ignition distributor. The latter mechanism turned out to be not reliable enough, and therefore in modern cars they began to actively use systems with individual coils belonging to each individual spark plug. In this regard, the sparking energy increased, and the level of radio interference created by the ignition system, on the contrary, decreased. Also, the use of this system made it possible to say goodbye to the need to use high-voltage wires, which often turn out to be unreliable.
The coil, as the most important element of the overall ignition system, needs special attention and care. Therefore, this should not be neglected and should be expected until the last moment, until only this mechanism fails, but also the entire ignition system, and later the car. So I recommend that you always find time to carry out at least basic diagnostics of the car and the ignition system in particular, especially if the principle of its operation is now known. And may the car never fail.
Video “Removing the ignition coil”
After watching the recording, you will learn how to remove the ignition coil yourself.
The ignition coil is an important part of the vehicle's starting system. Without its use, it is impossible to get the engine to start. It is impossible to start the engine without a battery, since the first spark will not form.
The structure of this part is quite simple, but from time to time, like other parts and elements of the car, it fails. The cause may be a malfunction or a certain manufacturing defect. The operation of the coil is not limited to standard engine starting. If the device suddenly fails while the engine is already running, this will automatically lead to its complete stop.

Knowing the answer to the question of how to check the ignition coil is a simple and sure way to identify a faulty part and understand whether it needs to be replaced or not.
Purpose
The main purpose of ignition coils is to transform low-voltage electrical current, which is obtained from the battery or generator, into a special electrical pulse with a sufficiently high voltage. Due to this process, the spark plugs produce the spark necessary to start the engine.
Principle of operation
The operating principle of the described device is quite simple. A low-voltage voltage is supplied to the primary winding of the coil, creating a magnetic field. Sometimes such voltage is completely cut off by a breaker, thereby contributing to a sharp reduction in the magnetic field and the formation of optimal electromotive force in the turns of the ignition coil.
According to the law of physics on electromagnetic induction, the indicator of the generated electromotive force is directly proportional to the number of turns of the circuit. It is for this reason that a high voltage pulse appears in the secondary coil, where there are more turns. It passes through high-voltage wires and is supplied to the spark plug. Thanks to this impulse, which is transmitted by the coil, a spark appears between the electrodes of the spark plug, igniting the air-fuel mixture.
In older car models, the voltage from the ignition coil was transmitted to the spark plugs via an ignition distributor. Such a scheme was not reliable, therefore the spark plug ignition coils of more modern cars are combined into a special system and distributed strictly one for each spark plug.
Types of coils
At the moment, there are three main types of ignition coils. Each of them is characterized by its own design features and requires more careful consideration:
- classic ones, which are used on cars with ignition systems with a distributor;
- two-terminal - used in a standard ignition system with direct supply of electrical voltage;
- individual - in this system there is one coil for each candle.
All three types are similar in design, with the exception of some nuances. The classic version consists of two windings - secondary and primary. The second one is placed inside the first one. The difference between the windings is the number of turns of wire used, as well as the thickness of the wire.
In the inner part of these windings there is a core made of a ferromagnetic alloy. Each winding has two terminals. In the primary, they are both input. In the secondary, one terminal is the output, and the second is connected to the primary winding. All of the above elements are placed in a sealed housing. As for the leads, they go out onto the housing cover.
The two-terminal coil differs from the classic version in the presence of two cores - the internal one, which is placed in the windings, and the external one, which is located above them. Instead of one high-voltage terminal of the secondary winding, such a coil has only two of them.
As for the individual coil, it differs in that not the primary, but the secondary winding is placed on top. In this case, its high-voltage terminal is connected to a special tip that is put on the spark plug terminal.
All types of coils are non-separable and cannot be repaired. These elements must be checked and replaced in a timely manner. This is very important, since a break or short circuit of the windings can cause malfunctions and also lead to complete inoperability of the engine.
Main ignition coil malfunctions and their causes
There may be several reasons for various malfunctions in the ignition coils. Among the most common of them are the following:
- Short circuit in the internal part of the device.
- Overheating of the coil due to its gradual wear.
- Increased coil charging time. This occurs due to a low voltage source, that is, a weak battery. This subsequently leads to premature wear or increased load on the ignition control unit.
- Violation of the tightness of components in the engine. Leaks can cause a short circuit, thereby causing a malfunction in the overall ignition system.
You need to know the reasons for failure of ignition coils. If you do not eliminate them, there is a risk of encountering rapid failure of newer elements.
Symptoms of malfunctions, or what you should pay attention to
Whatever type of coil is installed in the vehicle, after a certain period of operation it may fail.
The following symptoms of a faulty ignition coil can be identified:
- weak acceleration;
- loss of power;
- erroneous indicators on the instrument panel;
- switching the engine to safe-mode;
- The most serious sign of spark plug failure is that the engine will not start.
The listed signs of a malfunction of the ignition coil can appear both under a certain engine operating mode and in a constant mode.
Instructions for checking the ignition coil with a multimeter
Verification of the described element is a three-step process. It starts with careful preparation. Then a visual inspection is carried out and everything ends with testing the system using special instruments.
The functioning of the coil can be checked on professional diagnostic stands in special services and dealership centers. To do this yourself, you will need to use a multimeter. This tool is a universal diagnostic device with the widest possible range of applications.

Preparatory operations
Before you begin diagnosing the ignition coil itself, you will need to prepare a multimeter. This device is able to determine accurate voltage readings and the level of electrical resistance in Ohms.
Modern cars have different types of ignition coils. The parameters of each model are indicated by the PTS of each car. Such indicators need to be known so that diagnosis can be made. The test consists of identifying such a parameter as the resistance of the ignition coil, that is, the resistance of the secondary and primary windings. If during the verification process it is not possible to detect resistance indicators, it will be possible to rely on generally accepted signs.
Visual inspection
External system characteristics may vary slightly depending on the model. The following characteristic elements differ:
- lid;
- frame;
- centrally located terminal;
- two contacts.
During the visual inspection of the element, you will need to carefully examine the condition of the body and try to detect cracks, chips and burnt areas on the surface. Due to the fact that the body is made of hard rubber and, accordingly, does not allow current to pass through, the malfunction of the device will mostly be associated with internal damage.
If, in the process of studying the state of the external characteristics of the coil, certain problems are identified, the element will need to be replaced with a new one. The new coil must strictly comply with all the necessary technical characteristics - winding resistance, duration and spark energy. If no problems with external characteristics are detected, you can proceed to checking the primary and secondary windings.

Checking the primary winding
At this stage, you need to connect the multimeter to the negative and positive terminals, and set the device to measure the resistance level. Despite the fact that devices from different cars are characterized by different resistance levels, the indicator fluctuates in the range of 0.4 - 2 ohms.
If during the diagnostic process the device displays a value within this range, we can judge the serviceability of the device. The display of a value of 0 Ohm directly indicates that a short circuit has occurred in the winding. If the resulting value is infinity, a break has occurred in the electrical circuit. After checking the primary winding, you can begin to detect problems with the secondary.
Checking the secondary winding
During this test, the multimeter probes will need to be connected to the positive contact and to the high voltage wires. If the device has a special plate core, the resistance parameters will be in the range of 6 - 9 kOhm. All other coil categories will exceed 15 kOhm.
Comparison of measurement results with normalized values
After checking and determining the resistance level of the two categories of windings, all the readings obtained must be compared with the standard parameters established by the manufacturer. Thoroughly checking a dual coil is a more difficult task. The primary winding in coils of this type is connected directly to the connector.
The standard double coil circuit is somewhat different from the usual one and knowledge of it is necessary in the process of checking the primary winding. The secondary winding will ring without any problems. For this purpose, it is enough to simply connect the tester to a pair of high-voltage terminals.
Coil defects that are not detected by the tester
In addition to problems with the winding, which can be determined using a multimeter, there are other defects that cannot be determined using this device. Most of them are determined through external examination.
Problems of this kind include contact failure and oil leakage due to strong vibration. Elementary overheating of the coil may indicate a violation of its tightness.
Regardless of the detected malfunction, the coil cannot be repaired. All you can do is replace the part with a new element.
conclusions
An automobile ignition coil can be classified as an ultra-precise and fairly sensitive device. Any, even the most insignificant deviation from the norm can lead to quite serious breakdowns and malfunctions of vehicle components during its subsequent operation. Do not also forget that the coil is a device that cannot be repaired. If any faults are found, the part will need to be completely replaced.
(9
ratings, average: 4,22
out of 5)
The ignition coil is used as a high-voltage step-up transformer - a storage device for electrical energy in inductance, to create an arc discharge on the electrodes of the spark plug, lasting 1-3 ms.
The principle of operation of the ignition coil
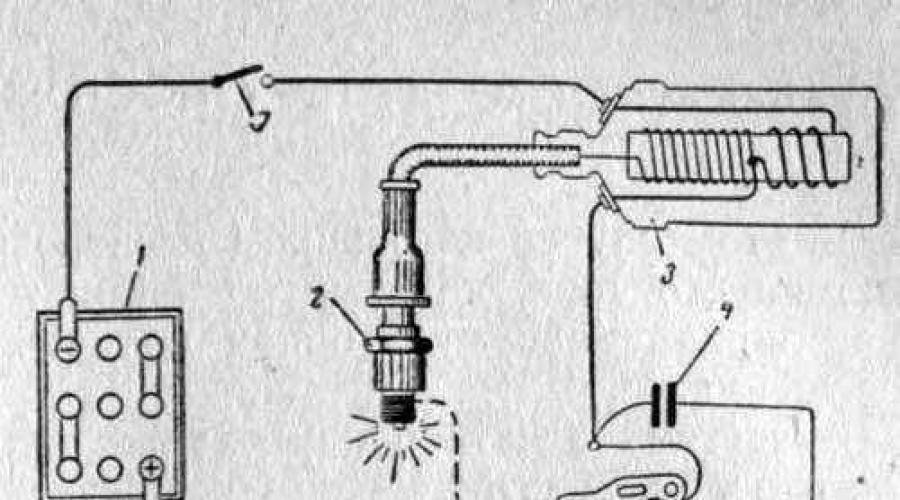
Rice. Sectional view of the ignition coil: 1 - insulator; 2 - housing, 3 - insulating paper, 4 - primary winding, 5 - secondary winding, 6 - primary winding output terminal (designations: “1”, “-“, “K”), 7 - contact screw, 8 - central terminal high voltage, 9 - cover, 10 - power terminal (designations: “+B”, “B” “+”, “15”), 11 - contact spring, 12 - bracket, 13 - outer wire, 14 - core.
The figure shows a cross-section of the ignition coil and one of the winding connection diagrams. Let's repeat what was stated earlier: coil is a transformer with two windings wound on a special core.
First, the secondary winding is wound with a thin wire and a large number of turns, and on top of it the primary winding is wound with a thick wire and a small number of turns. When the contacts are closed (or in another way), the primary current gradually increases and reaches a maximum value determined by the battery voltage and the ohmic resistance of the primary winding. The increasing current of the primary winding meets the resistance of the emf. self-induction directed counter to the battery voltage.
When the contacts are closed, current flows through the primary winding and creates a magnetic field in it, which crosses the secondary winding and a high voltage current is induced in it. At the moment the breaker contacts open, an emf is induced in both the primary and secondary windings. self-induction. According to the law of induction, the greater the secondary voltage, the faster the magnetic flux created by the magnetic current of the primary winding disappears, the greater the ratio of the number of turns, and the greater the primary current at the moment of break.
This design is typical when building ignition systems using breaker contacts. The ferromagnetic core can be saturated with the primary current, which would lead to a decrease in the energy accumulated in the magnetic field. To reduce saturation, an open magnetic circuit is used. This allows you to create ignition coils with a primary winding inductance of up to 10 mH and a primary current of 3-4 A. Higher current cannot be used because At this current, the contacts of the breaker may begin to burn.
If the inductance in the coil is Lk = 10 mH and the current I = 4 A, then the energy W in the coil can be stored no more than 40 mJ with efficiency = 50% (W = Lk * I * I/2). At a certain value of the secondary voltage, an electric discharge occurs between the electrodes of the spark plug. Due to the increase in current in the secondary circuit, the secondary voltage drops sharply to the so-called arc voltage, which maintains the arc discharge. The arc voltage remains almost constant until the energy reserve becomes less than a certain minimum value. The average duration of battery ignition is 1.4 ms. This is usually enough to ignite the air-fuel mixture. After this, the arc disappears; and the residual energy is spent on maintaining damped voltage and current oscillations. The duration of the arc discharge depends on the amount of stored energy, mixture composition, crankshaft rotation speed, compression ratio, etc. As the crankshaft rotation speed increases, the time of the closed state of the breaker contacts decreases and the primary current does not have time to increase to the maximum value. Because of this, the amount of energy accumulated in the magnetic system of the ignition coil decreases and the secondary voltage decreases.
The negative properties of ignition systems with mechanical contacts appear at very low and high crankshaft speeds. At low rotation speeds, an arc discharge occurs between the breaker contacts, absorbing part of the energy, and at high rotation speeds, the secondary voltage decreases due to the “bouncing” of the breaker contacts. Contact systems have not been used abroad for a long time. Cars produced in the 80s are still driving along our roads.
Some ignition coils work with an additional resistor. A functional diagram of connecting such a coil to a contact ignition system is shown nearby.

Rice. Connection diagram of the ignition coil with the contact ignition system: 1 - spark plugs, 2 - distributor, 3 - starter, 4 - ignition switch, 5 - starter solenoid relay, 6 - additional resistance, 7 - ignition coil.
The connection diagram of the coil windings is different. During starting modes, when the voltage on the battery drops, the additional resistor is short-circuited by the auxiliary contacts of the starter solenoid relay or the contacts of the additional starter activation relay, which provides the primary winding of the ignition coil with an operating voltage of 7-8 V. At engine operating modes, the supply voltage is 12-14 V. The additional resistor is usually wound from constantan or nickel wire. If the wire is nickel, then such resistance is called a variator due to the change in resistance depending on the amount of current flowing through it: the greater the current, the higher the heating temperature and the higher the resistance. At increased crankshaft speeds, the strength of the primary current drops, the heating of the variator weakens and its resistance decreases. Tzh. Since the secondary voltage depends on the rupture current in the primary circuit, the use of a variator makes it possible to reduce the secondary voltage at low speeds and increase them at high engine speeds.
In transistorized ignition systems, the primary current is interrupted by a power transistor. In such systems, the primary current is increased to 10 - 11 A. Ignition coils with low primary winding resistance and high transformation ratio are used. We present samples of oscillograms taken in a working system on the primary and secondary windings of the ignition coil.

Rice. Oscillogram of the primary winding.

Rice. Oscillogram of the secondary winding.
The shape of the oscillograms is very similar, because The coil windings are interconnected by a transformer connection (mutual induction). The coils of contact-transistor and transistor ignition systems have a classic design: oil-filled, with an open magnetic circuit, in a metal case. Let's give some data on produced domestic ignition coils.

As shown in the table, ignition coils differ in the number of turns in the windings and the transformation ratio in various ignition systems. The coil designs differed little.
Location
Under the hood on the fender or on the dividing panel between the engine compartment and the vehicle interior. Sometimes directly on the engine.
Ignition coil malfunctions
The main malfunction is a break in the primary or secondary windings. Sometimes the emergency oil pressure valve is triggered due to overheating. After draining the oil, the coil fails. Some coils continue to operate even if the secondary winding is broken, and during throttling, misfires are observed.
During long-term operation of the vehicle, the insulating properties of the materials used in the ignition coils lose their properties and high-voltage burnouts occur, allowing part of the charge to “leave” to ground. When inspecting the ignition coil, such a malfunction can be easily detected by a gray mark on the surface of the coil insulator (similar to a mark from a simple pencil) or a black burnout with a partially charred surface.
It is necessary to inspect the connector of the high-voltage (HV) wire coming out of the ignition coil. In 70% of cases there is an oxidized surface or rust. In this case, be sure to check the central high-voltage wire. Its resistance should be no more than 20 kOhm. A not uncommon situation: it rings, the resistance is up to 20 kOhm, and the combustion oscillogram on all cylinders is equally incorrect. With sharp throttling, the combustion oscillogram is even more distorted, chaotic sparking is observed, and only replacing the central explosive wire brings a positive result.
Test method
Perform the check with a connected automotive oscilloscope. The waveform shapes are the same as those of microprocessor ignition coils. Measure the resistance values of the primary and secondary windings.